Energy Efficiency Meets Innovation: The Promise of Net-Zero Energy Buildings

In the quest for a sustainable future, Net-Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB) stand out as a beacon of innovation and environmental responsibility. As climate change accelerates and the demand for energy continues to grow, the construction industry faces immense pressure to adopt greener practices. NZEBs offer a compelling solution by balancing energy consumption with energy production, thereby reducing the overall carbon footprint. In this blog, we'll explore what NZEBs are, their benefits, and how they are shaping the future of construction.
What Are Net-Zero Energy Buildings?
Net-Zero Energy Buildings are designed to produce as much energy as they consume over the course of a year. This is achieved through a combination of energy efficiency measures and on-site renewable energy generation. The ultimate goal is to achieve a balance where the total amount of energy used by the building annually is equal to the amount of renewable energy created on-site or by renewable energy sources elsewhere.
Net-Zero Energy Buildings (NZEBs) are designed to minimize energy loss through the incorporation of advanced building materials and design techniques. They feature high-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows, and airtight construction, all of which significantly reduce the need for heating and cooling.
In addition to these efficiency measures, NZEBs often utilize renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems, to generate electricity and heat. By harnessing renewable energy, these buildings can greatly reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. Furthermore, the integration of smart building technologies, such as automated lighting, HVAC systems, and energy management systems, helps optimize energy use and maintain a balance between energy consumption and production. Finally, NZEBs emphasize the use of sustainable and locally sourced materials, which lowers the environmental impact associated with the extraction, processing, and transportation of building materials.
What are the benefits?
Environmental Impact
One of the most significant benefits of NZEBs is their positive environmental impact. These buildings play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, thus aiding the fight against climate change. By generating their own energy, NZEBs minimize dependence on non-renewable energy sources and contribute to a lower overall carbon footprint.
Economic Savings
While the initial investment in NZEBs can be higher than traditional buildings, they provide substantial economic savings in the long run. The reduced energy costs over time can offset the upfront expenses, making these buildings a financially viable option. Homeowners and businesses alike can benefit from lower energy bills, ultimately leading to significant cost savings.
Energy Independence
NZEBs also promote energy independence by generating their own power. This self-sufficiency reduces vulnerability to energy price fluctuations and enhances energy security, providing a more stable and predictable energy supply for occupants.
Enhanced Comfort and Health
The advanced design and technologies utilized in NZEBs contribute to enhanced comfort and health for occupants. These buildings typically offer better indoor air quality and maintain consistent indoor temperatures, leading to an overall improved living and working environment.
Latest insights & stories

Seven cybersecurity trends and threats for 2025
Last year saw another alarming increase in cyber-attacks, with hackers using increasingly sophisticated methods. Proximus NXT and its security partners explain how to navigate a minefield of vulnerabilities in 2025.
IT is innovating faster than ever. We should embrace the limitless possibilities in cloud adoption, generative and non-generative artificial intelligence and the increasing use of APIs, says our expert panel. At the same time, cyber criminals see such trends as opportunities to compromise businesses and are capitalizing on new vulnerabilities.
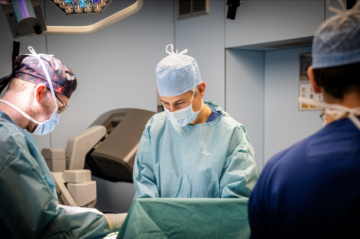
The az groeninge hospital innovates care with 5G
A private 5G network at az groeninge provides the platform for the hospital to roll out innovation. From remote monitoring with biosensors to robotic surgery and training using VR: everything is focused on patient care.

Why your AI project is also a data project
AI needs quality data to realize its full potential. Yashfeen Saiyid, Data & AI Practice Lead at Proximus NXT, explains how to use a data-driven approach to lay the foundations for a successful AI project.
“There are more and more business applications, these days, based on artificial intelligence. And the accelerating rise of generative AI, with ChatGPT as its flagship, is simply breathtaking. According to Gartner, 90% of companies will use AI in the workplace by 2025,” begins Yashfeen Saiyid, Data & AI Practice Lead at Proximus NXT and Managing Director at Codit.