3D printing plays a key role in the shift towards a more circular economy

3D printing has found its place in this world. It is a production technique that converts a digital file into a tangible, three-dimensional object by building it up from layers.
3D printing has found its place in this world. It is a production technique that converts a digital file into a tangible, three-dimensional object by building it up from layers.
3D printing has found its place in this world. It is a production technique that converts a digital file into a tangible, three-dimensional object by building it up from layers. Everything starts with an idea being developed in a computer program. The digital design is prepared for and sent to the 3D printer, which builds the object layer by layer. How this is done, can vary significantly depending on the 3D printing process being used.
In the past, 3D printing was known as Rapid Prototyping because it was mainly used to design prototypes. Nowadays, 3D printing is known as Additive Manufacturing, which makes it clear that something is added or built up, whereas with other production methods - such as laser cutting - things are cut away.
The benefits Additive Manufacturing offers
Faster go-to-market thanks to faster prototyping which saves a significant amount of time. Cost effectiveness in production thanks to a shorter production time. On top of that, the design and capability to manufacture parts with lightweight structures requires less material. Waste reduction since less materials are used during the production process. Additionally, a high degree of personalisation is possible and transport costs are being reduced as digital files can be shared globally in the form of virtual inventories and produced locally, instead of physically shipping finished parts and products. Thanks to 3D printing, companies can make their products themselves more quickly and they do not need to have them produced, for example, by a supplier in a low-wage country. That way they save time and reduce their CO2 emissions. It is the combination of speed, lower cost and sustainability that is making industrial 3D printers grow in popularity as a manufacturing method.
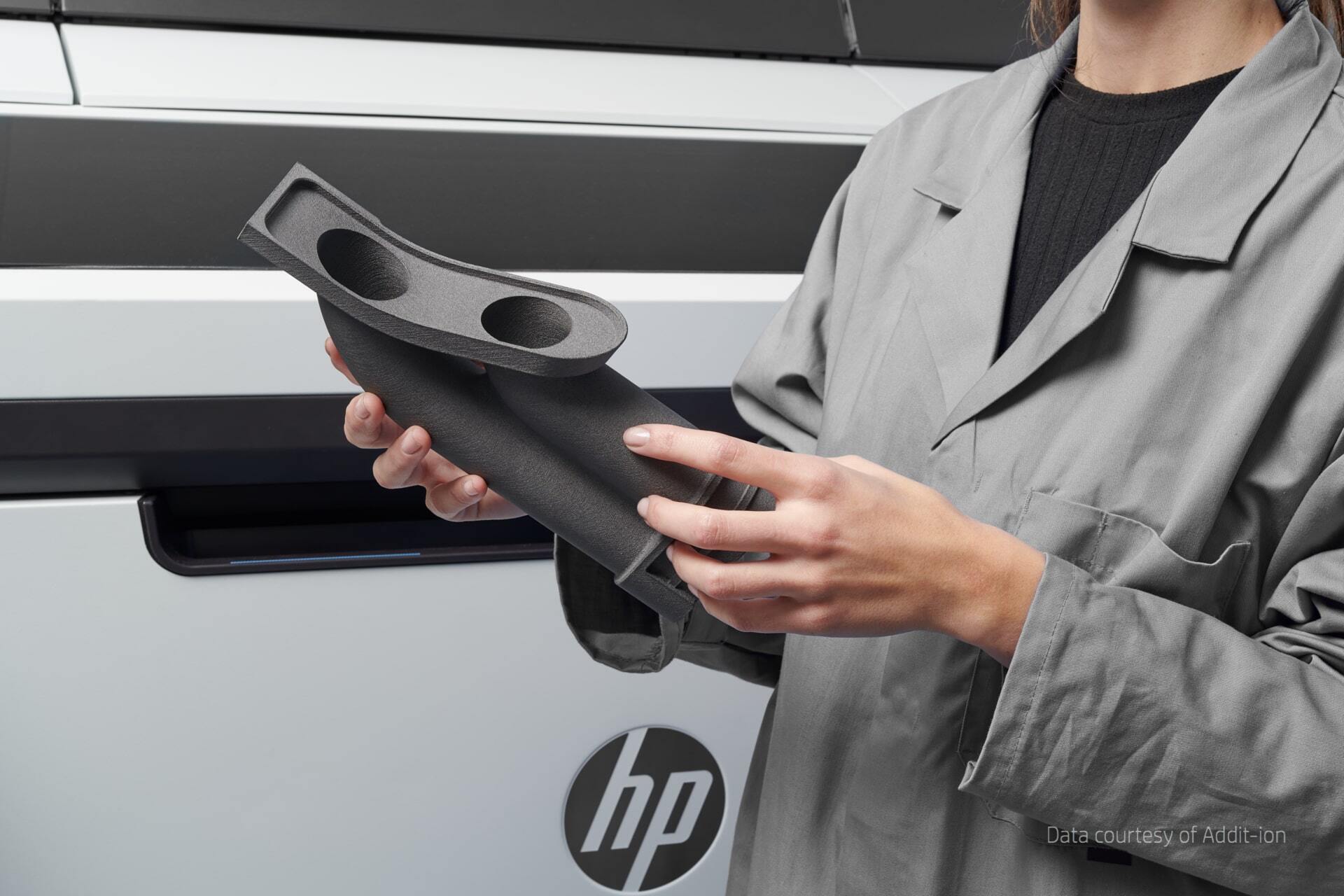

Where is 3D printing being applied?
The use of 3D printing is not limited to one single domain. The building sector uses Additive Manufacturing: the first fully 3D-printed house is to be found in Flanders. Important breakthroughs were achieved in the medical sector. HeyGears, an innovation-driven technology company, was able to create a 3D orthotic with a unique adjustable design that easily positions a patient’s wrist at different angles, ensuring movement of the wrist joint as well as gradual correction and protection of the joint. Traditional materials such as plaster and some polymers resulted in heavy orthotic devices that did not breathe well, making it difficult for the physician to adjust and clean. But 3D printed orthotics can be adjusted by the patient, reducing the number of necessary visits with the physician.

The automobile sector was the first to embrace the 3D printing technology. This way, HP 3D printing helped CUPRA Racing to create lightweight components for a new race car. CUPRA, a company within the SEAT organization that produces high performance vehicles including race cars, was faced with the challenge of quickly creating prototypes for some of the car’s lightweight components, like side mirrors, air vents and a central control module for the steering wheel. The organization identified the HP Jet Fusion 5200 Series 3D Printing Solution as the answer to the challenge. This enables CUPRA to produce multiple on-demand parts in order to test designs.
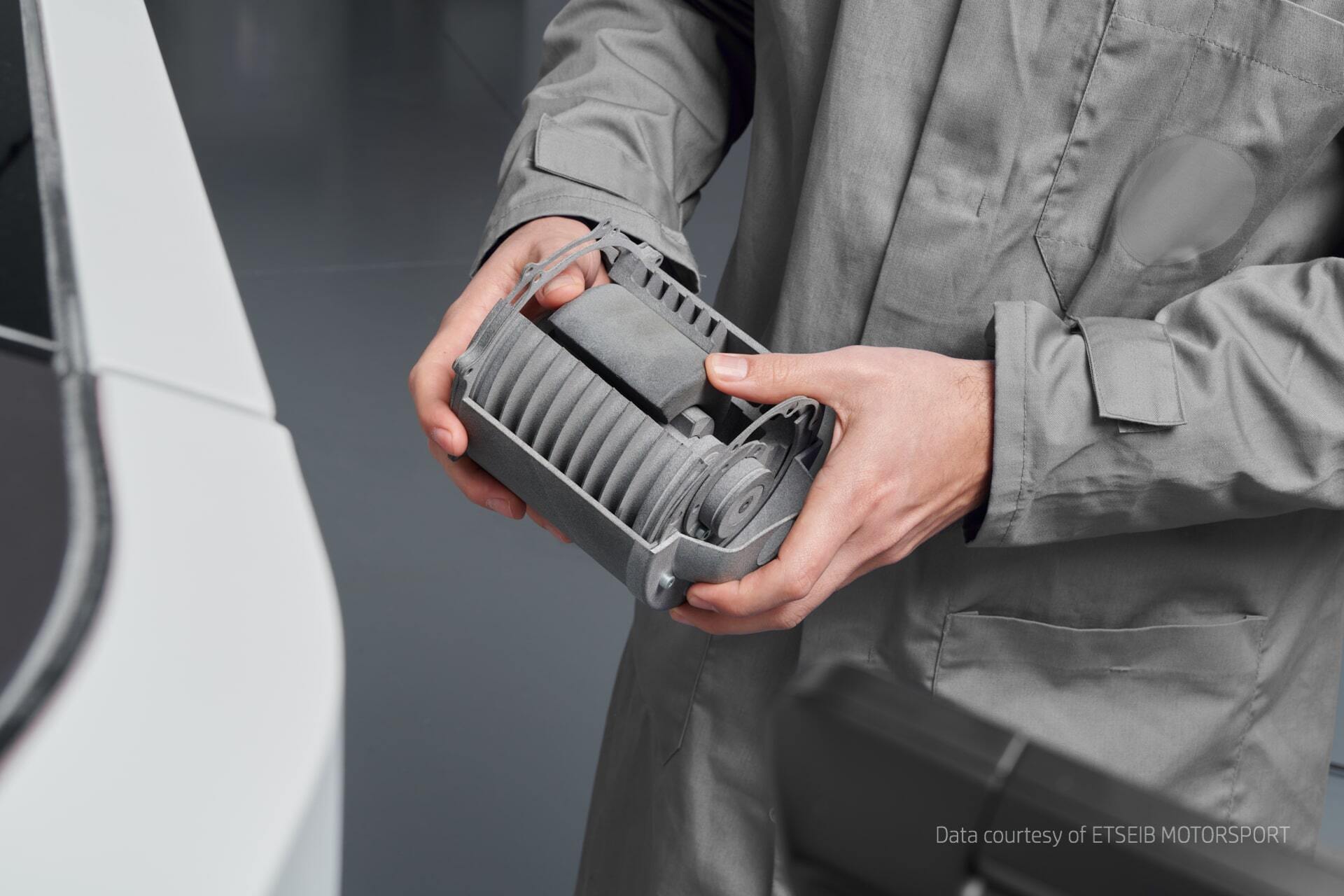

HP passionately believes in industrial 3D printing and can help companies with the HP Jet Fusion 3D printing solutions. That is why HP is also focusing on this innovative printing technology in the Office of the Future. In fact, during the COVID-19 pandemic, HP and some partners ensured that medical accessories such as hands-free door openers and face shields could be 3D printed quickly.
Obviously, HP 3D printers are already being used in many businesses. Discover the world of opportunities that you could unlock with 3D printing through specific user cases.
Latest insights & stories

AI and data integration: an indispensable symbiosis

Seven cybersecurity trends and threats for 2025
Last year saw another alarming increase in cyber-attacks, with hackers using increasingly sophisticated methods. Proximus NXT and its security partners explain how to navigate a minefield of vulnerabilities in 2025.
IT is innovating faster than ever. We should embrace the limitless possibilities in cloud adoption, generative and non-generative artificial intelligence and the increasing use of APIs, says our expert panel. At the same time, cyber criminals see such trends as opportunities to compromise businesses and are capitalizing on new vulnerabilities.
The az groeninge hospital innovates care with 5G
A private 5G network at az groeninge provides the platform for the hospital to roll out innovation. From remote monitoring with biosensors to robotic surgery and training using VR: everything is focused on patient care.